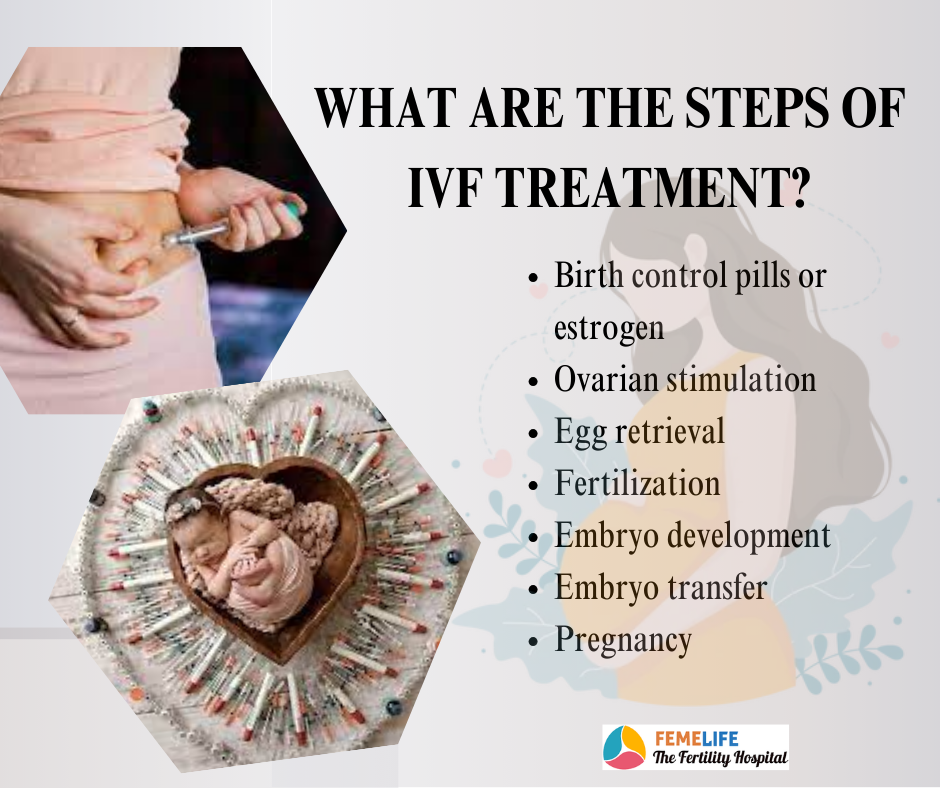
Seven steps of IVF procedure
- Down regulation
- Ovarian stimulation
- Ovulation trigger
- Egg retrieval and Sperm aspiration
- IVF laboratory process
- Embryo replacement
- Hormone support after embryo transfer
Down regulation before IVF procedure
This is a procedure by which pituitary gland is stopped from controlling the ovary. As a result, it reduces the risk of a cycle being cancelled by luteinising hormone (LH) hormone. LH hormone can disrupt normal follicle and oocyte development. Moreover, it can stimulate premature release of the eggs before they can be collected in the laboratory.
Ovarian stimulation
This aims at producing a number of mature eggs which can be collected for fertilization in the laboratory. It is done by giving daily injections for 10- 12 days. Hormones like FSH and LH are given as shots in various combinations. The dose and duration is decided by ultrasound and hormone monitoring of cycle.
Ovulation trigger in IVF procedure
After the growth of follicles, at the end of the stimulation phase maturation of eggs is important. In an IVF cycle, eggs are collected after the ovulation trigger. HCG is an hormone which is used to mimic the natural endogenous LH surge. As a result, the process of ovulation id initiated. Then, mature eggs are collected from the woman and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory.
Oocyte and sperm retrieval
After triggering, mature oocytes are aspirated from the woman’s ovaries for fertilization in the laboratory. Egg harvesting can either be done under direct vision laparoscopically or by ultrasound. Since, transvaginal oocyte retrieval is unpleasant and painful effective anaesthesia or analgesia is provided to minimise adverse effects.
In addition, in some cases of male factor infertility the sperm has to be obtained directly from the testes. Surgically collected sperm in azoospermia are immature. Hence, have low fertilizing ability with standard IVF. It is therefore necessary to use ICSI.
IVF Laboratory Process
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a complex series of procedures used to achieve fertilisation. IVF or ICSI is the most effective form of assisted reproductive technology. IVF/ICSI aims at achieving fertilisation and embryo development through hi-tech laboratory equipment and skilful techniques. In IVF, the eggs are mixed with partner’s sperm in a dish to achieve fertilisation. ICSI is an advanced procedure where a sperm is injected into an egg through an inverted microscope with manipulator. ICSI achieves higher fertilisation than IVF procedure.
Embryo Culture And Replacement
IVF aims for a woman to have a healthy baby delivered safely at term with minimum risks. However, this procedure is associated with a risk of multiple pregnancy and harm for both mother and babies. After IVF procedure embryos are cultured in the laboratory for optimal growth. Once the embryos are ready patients return to the IVF facility for embryo transfer. Embryo transfer is a quicker and easier procedure than retrieval of eggs. The doctor inserts a flexible thin catheter into the uterus through which embryos are deposited.
Hormone support after embryo transfer
In a normal menstrual cycle, once ovulation has occurred, the endometrium prepares to receive a fertilized embryo. However, during IVF procedure use of hormones to block the activity of the pituitary gland can result in inadequate production of support hormones. Hence, in IVF the luteal phase needs to be supported by means of progesterone, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and other medication. Luteal phase support with progesterone is associated with significantly more live full-term singleton births.