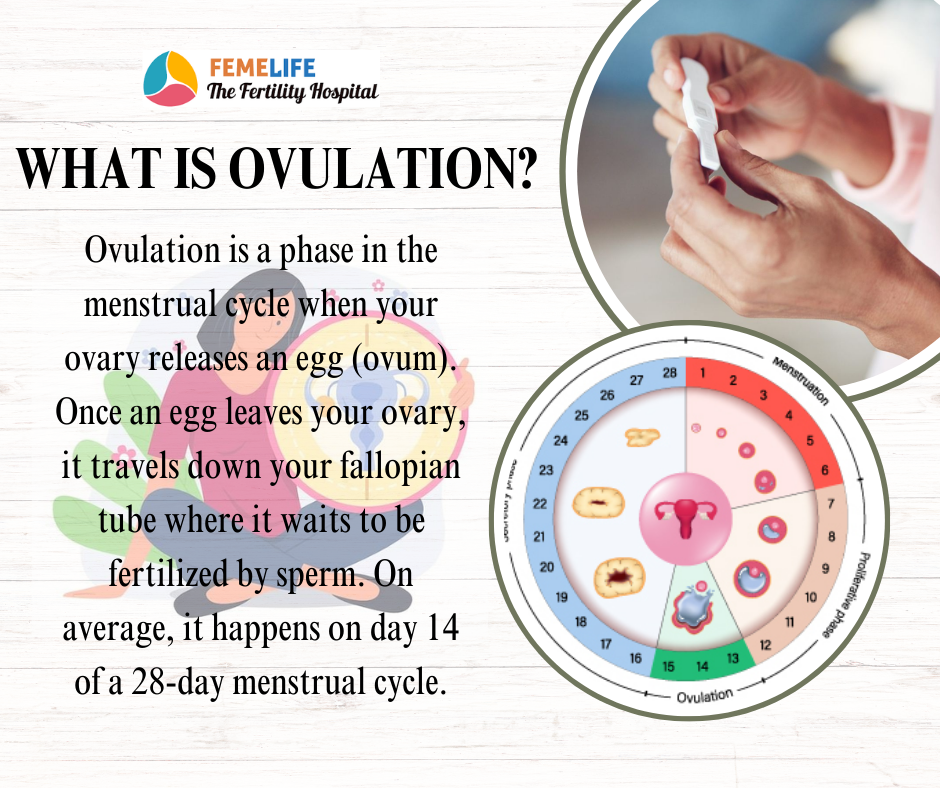
What is ovulation?
Ovulation is a menstrual cycle phase in which your ovary produces an egg (ovum). Once an egg has left your ovary, it travels down your fallopian tube to be fertilised by sperm. It usually occurs on day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
Ovulation and your menstrual cycle
When your hypothalamus (a component of your brain) releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), the process of ovulation begins. GnRH stimulates the pituitary gland (a brain gland) to produce follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
FSH induces follicles (small sacs of fluid in your ovaries that contain a developing egg) in one ovary to mature between days six and fourteen of your menstrual cycle. Only one of the maturing follicles produces a completely developed egg between days 10 and 14 of the cycle.
A increase in LH around day 14 of the menstrual cycle prompts the ovary to discharge this egg. This is the process of ovulation. Following ovulation, the hormone progesterone rises, which aids in the preparation of your uterus for pregnancy.